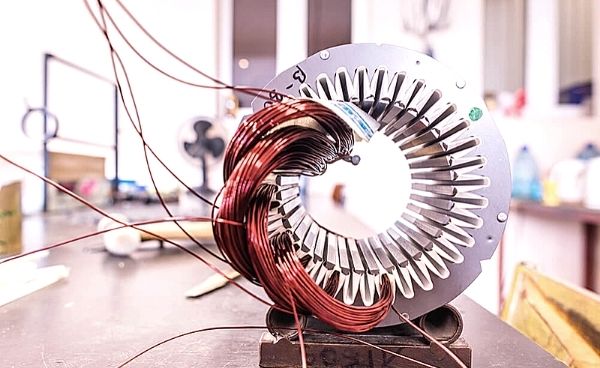
Why Winding Resistance Test is Important for the Motor?
Winding resistance test measurements detect various faults in motors and transformers: shorted turns, loose connections, broken strands, and malfunctioning tap changer mechanisms.
Studies conducted by IEEE and the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) on electric rotating machinery failures show that 48% of motor failures are due to electrical failures.
Winding resistance test measurements detect problems in motors that other tests may not find.
These problems include:
1. Partial or fully shorted coils.
2. Poor crimps or connections.
3. Imbalance between phases (improper turns on phases) and incorrect coil (phasing) connections.
Winding resistance testing method:
Winding resistance tests are a measurement of the applied DC voltage and current to the device under test – DUT. Using Ohm’s law the resistance is calculated in µΩ (micro Ohms) or mΩ (milli Ohms) by the winding analyzer.
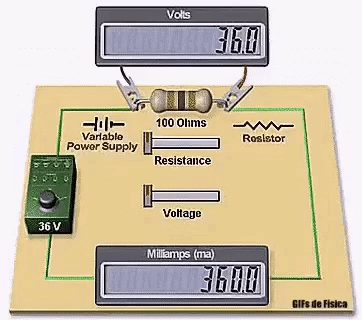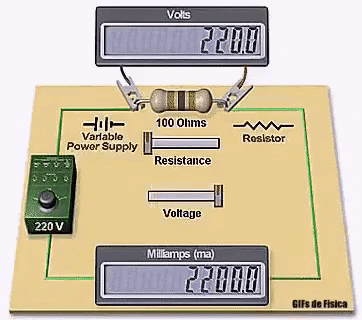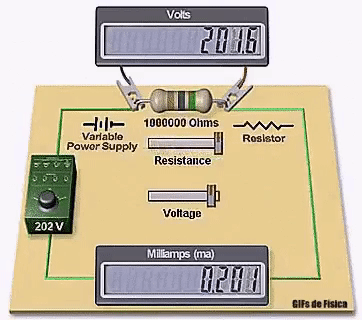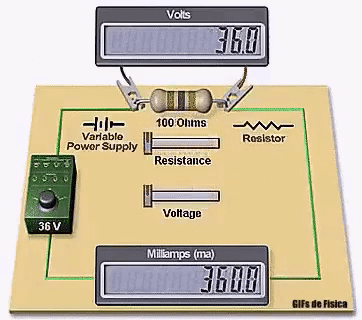
For a 3-phase motor, 3 resistance measurements are normally done between the phases, and the balance or imbalance between the 3 measurements is calculated and displayed along with the measurement values.
For single coils and sometimes for motors, the resistances measured may be compared to a resistance value instead of having a balance calculated. The difference in percent to the target resistance value is then calculated.
A temperature correction factor can automatically be applied to correct the measurement to a standard temperature so results can be more accurately tracked over time with the winding analyzer.
source: electrominst.com
Aarohi Winding Resistance Test Meter
AAROHI resistance meter measure a wide range of resistance values at a high level of accuracy.
RR2204CZZ is a high-precision, portable resistance meter capable of measuring resistance with extremely high accuracy with low ambient temp. effect.
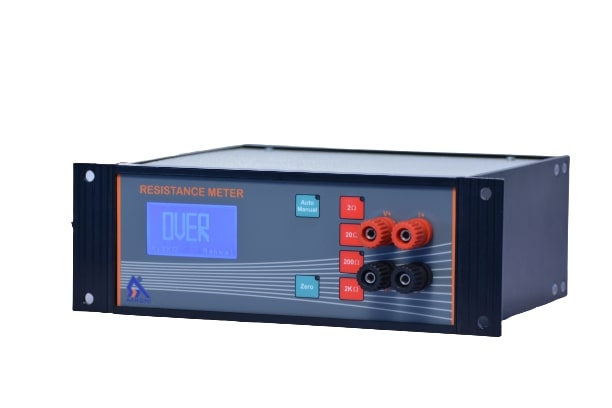

This is ideal for the testing and maintenance of
- Electric motors,
- Pump sets & other equipment with windings.
This Instrument is based on the Kelvin 4- wire connection method for the measurement of low resistance.